

Or, they may have to offer significant advantage to counter these switching costs at their own expense. If there are significant switching costs, then a new entrant may not be able to create means of removing these.

These include access to the best suppliers, an understanding of existing materials and knowledge of their quality, possession of any necessary and important patents, and proprietary information and technological knowledge.

Economies of Scale: When manufacturing or selling at a large scale, companies are able to avail cost advantages because per unit costs of the product fall.There are many types of barriers to entry into a market. Most of these can be categorized within the potential barriers to entry that exist for that industry. There may be many ways to determine whether there is an active threat to a market or industry from new entrants. Control: Existing firms may choose to control how a new firm enters the market rather than attempt to stop any new competitors from emerging.Demand: Increased demand may result in increased prices thereby allowing a new entrant to make use of this increase and offset any high costs of market entry.Competitive advantage: Foreign based competition, through development of a specific competitive advantage can also be a threat.Diversification: Product diversification from existing firms into other categories.This firm may bring new and innovative expertise to the industry, thus changing the competitive dynamics for everyone. Take-over: A company from outside the industry may take-over an existing firm, thereby avoiding any of the traditional barriers to entry within the firm.How a new firm enters a market can happen in a number of ways:
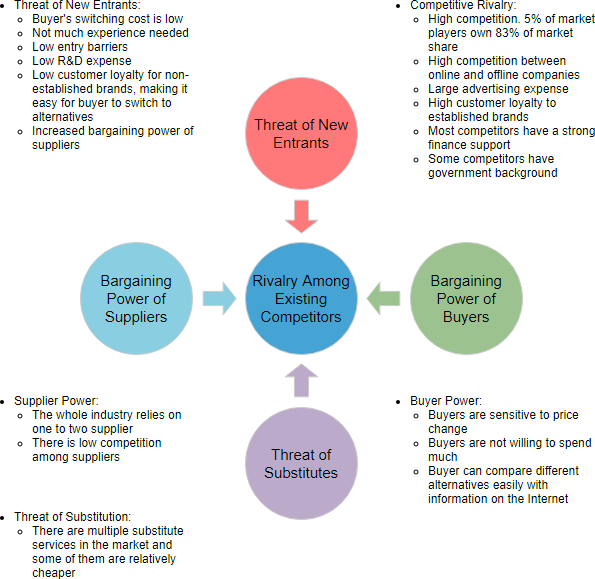
Sales and market shares will be redistributed and there may be an effect on price and product quality. This is because more competitors will fight for the same amount of business. If there is a higher threat of new entrants, this means that there are low barriers to entry and there is high possibility that the industry profit potential will decrease as a whole. According to his model, this threat changes the competitive environment and directly impacts the profitability of an existing firm. Porter’s definition helped people see this threat as substantial and influential. Porter believed that the possibility of new entrants had a significant part to play in developing and changing the competitive dynamics of any industry. In this article, we will look at an 1) introduction to the threat of new entrants, 2) determining the nature of the threat, 3) responding to new entrants – strategic entry deterrence, and 4) an example of and the threat of new entrants. © Entrepreneurial Insights based on the concept of Porter’s 5 Forces


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
